Automatic translation
Machine translations with post-editing
- Machine translation (MT) in 70 languages
- Quality assurance in accordance with DIN ISO 17100 and DIN ISO 18587
- Consulting: AI workflows tailored to your content
Automatic translation of your texts
Translation agency with AI experience
Automatic translation, yes or no? These days, cost-cutting measures are at the top of many managers’ lists of priorities. Interest in machine translation (MT) and AI is greater than ever.
- “How much can I save with machine translation?”
- “What is the quality of MT and for which texts can I use it?”
- “Can large language models (LLMs) take over quality control?”
These are some of the questions that many people are asking today. We provide you with concrete answers and decision-making aids here.
Machine translation has improved significantly, especially with technologies such as Google Translate, DeepL and Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. The cost of a post-edited machine translation depends heavily on the amount of post-editing work required. However, for many projects, the cost can be reduced to around 60-70% of the cost of a new translation.
The quality of machine translation today is better than in the early years of neural machine translation systems. Some MT systems now allow the integration of terminology, which further improves the accuracy and consistency of translations.
D.O.G. has been actively involved in machine translation since 2008. A joint research project with the French university ISIT resulted in functions in our quality assurance software ErrorSpy that enable errors to be better recognised and corrected by translation engines. Today, we use this experience to offer our customers the best possible translation solutions.

AI translation into all languages
Translate your texts and apps into all languages—automatically
Do you need an automatic translation of web pages? Or would you like to have a Google Translate translation checked? We will send you a quote within a very short time.
Automatic translation with AI-supported post-editing (LLMs)
All-round solution for machine translation
Automated translation has long been a reality – with neural networks, large language models (LLMs) and specialized engines. However, not every text is suitable for a fully automated solution. The trick is to classify content according to risk and target group and select the appropriate translation process.
D.O.G. helps companies to use machine translation safely and efficiently –without black box risks. Instead, we rely on a combination of consulting, selection of the right tools and quality assurance.
Our approach: using machine translation and AI where they make sense.
We work with you to design risk-based translation workflows tailored to your content types. These workflows save time, ensure quality, and flexibly scale with your content volume. Our approach combines proven tools like DeepL with the latest AI technologies—always controllable, transparent, and fully traceable.
What sets us apart:
- We work with open machine translation systems—so you stay in control and can customize them to your needs.
- We support you in using generative AI effectively – for example with customized prompts for your processes.
Challenges of machine translation
AI and MTPE: We have the necessary knowledge
Automatic translation yes, but not for all texts
Companies produce and use a whole lot of information. They serve different purposes (pure information and communication, advertising, operation of machines, etc.), are legally binding or not (such as the operating instructions specified by the new machinery regulation (EU) 2023/1230 (MDR), which has been the successor to the European Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC since July 2023). They are formulated in a demanding or highly standardized way.
Depending on these features and criteria, machine translation is recommended or human translation is preferred. You can find more information on machine translation and its limitations in this blog article: Fully automated translations: Dream or soon to be reality? (in German).
Basically, you need to know that machine translation works better when:
- the topic and language pair have already been learned by the translation engine. This learning occurs during the machine training phase, in which a substantial amount of bilingual text—typically segment pairs from translation memories—is processed by the deep learning algorithm.
- quality compromises compared to human translations are justifiable: a correct translation is not necessarily a good translation. In addition, the residual risk of a mistranslation is greater with MT than with human translators.
- the quantities of texts are sufficient to operate the system economically.
- the text is written simply: short sentences, hardly any ambiguity, standardised terminology and syntax. Better still, the author knows how MT works and writes texts that are optimised for machine translation.
- the text is for information purposes only. This applies, for example, in internal communication—when someone simply needs to understand the content of a document or email. Typical cases include technical customer service needing to determine what kind of issue needs to be addressed.
- the time factor is paramount: MT is clearly faster, even with post-editing.
MT is not necessarily a competitor to translation memory systems. Rather, it is another tool that can be used to produce translations.
Machine translation: the most common mistakes and challenges
Human translators and machine translation systems both make mistakes—but the types of errors often differ. MT systems may translate proper names, do not understand many abbreviations and may even add information that is not present in the original text. Sometimes they also omit words from the translation. Such errors are not always easy to recognise, especially if the translated sentence otherwise sounds fluent and correct. We have provided an overview of typical errors in machine translation systems in this article (in German) in the tekom magazine.
This is why we at D.O.G. offer a combination of machine translation, AI-supported quality assurance and human review. We utilise the speed and efficiency of machine translation, complemented by the accuracy and understanding of human translators. This allows us to take advantage of the benefits of both approaches while minimising their weaknesses.
We ensure terminology control by predefining relevant terms—either through glossary uploads for MT engines or structured prompts for LLMs. This helps to improve the accuracy and consistency of translations and minimise some of the most common sources of error. Our aim is always to provide our customers with the best possible translation results.
This is why it is important to train post-editors and to inform them about the types of errors they need to look for. The typology of these errors differs depending on the type of translation engine used: statistical machine translation (SMT) systems make different errors than neural machine translation (NMT) systems.
Since it was founded over 25 years ago, D.O.G. has been working intensively on the topic of translation quality and, since 2008, specifically on the quality of machine translation systems. We have developed our own tools and metrics to check this quality. Before the machine translation starts, we identify the segments that are not suitable for the MT process and sort them out or flag them for further processing steps.
You can benefit from our experience.
Costs and benefits of automatic translations
The introduction of machine translation is no longer a complex, large-scale IT project – but a strategic decision about where and how AI technology can be meaningfully integrated into existing translation processes. Instead of in-house model training with high data and resource requirements, modern companies are increasingly relying on existing, powerful systems that are tailored to their needs through targeted configuration, data preparation and quality assurance.
Instead of investing in the development of in-house engines, the key today lies in the intelligent use of open systems – be it through interface connection (API), prompting strategies, terminology control or hybrid workflows with post-editing.
The costs are therefore no longer incurred by GPU-supported training runs, but rather by:
- Initial analysis and planning, e.g. through content classification, risk assessment and selection of suitable workflows
- Tool integration, e.g. of existing MT engines, LLMs, terminology and QA tools (such as LookUp, ErrorSpy etc.)
- Prompt engineering, i.e. the development and optimization of instructions for generative AI, adapted to text type, style and terminology specifications
- Quality assurance and process control, including post-editing, automated checks and feedback loops
- Optional: Technical infrastructure (e. g. on-premise solutions or dedicated APIs) if this is required for data protection or compliance reasons
The benefit lies in the sustainable relief of resources, shorter throughput times, greater consistency and better scalability as content volumes increase. When used correctly, machine translation can save between 30% and 50% in time and costs – without compromising on quality and terminology accuracy.
We would be happy to help you identify economically viable areas of application, quantify specific potential and develop a solution that delivers real value in your day-to-day operations.
Operation and Utilization of the System: The system must continue learning from its mistakes and be trained with new topics and data during the deployment phase. Additionally, post-editing costs must be factored in, as they reflect the time and effort editors spend correcting machine-generated errors. We calculate setup costs (one-time implementation fees) separately from ongoing usage costs. This means you benefit from a per-word rate for operational use that is lower than the cost of human translation. Once the key parameters for your solution are defined, we’ll be happy to provide a detailed quote.
The cost-effectiveness of a machine translation (MT) solution ultimately depends on how it is deployed. If you are already achieving substantial savings through translation memory systems and plan to apply MT to the same content types, additional savings may be limited. However, if you’re translating new content that hasn’t previously been processed—or has only been translated without the aid of technology—then MT can rapidly become a highly cost-effective solution.
Your quality-checked automatic translation in 6 steps
Your Path to an AI-Powered Translation Solution—with D.O.G.
You’re looking to reduce translation costs using machine translation—but you may have concerns about quality and the risk of serious errors. At D.O.G. GmbH, we combine AI-powered translation with the expertise of experienced post-editors to ensure reliable results. In addition, we use large language models and advanced AI methods to detect and correct errors in style or meaning that may occur in machine-generated output. Here, we’ll show you how we work with you to develop a robust, high-quality machine translation solution you can trust.

What do you want to achieve?

Classify and prioritise content

Select systems and tools

Prepare language data & terminology

Set up and secure workflows

Applying the AI solution
Depending on your goals, different workflows and implementation strategies may be required. Our team of specialists and software developers will help you to implement the right solution.
Automatic translation with post-editing for various industries
We use machine translation software in these industries
These are some of the industries in which we offer machine translation:
Automatic translation into English and other languages
Automatic translation with post-editing in these languages
We offer a wide range of language combinations for the machine translation of your content. Here are some of the most requested language pairs:
- Machine translation German → English
- Machine translation English → German
- Machine translation German → Spanish
- Machine translation Spanish → German
- Machine translation German → French
- Machine translation French → German
Quality of automatic translations
Our goal with MT: quality and time savings

Ensuring quality - before errors occur
Many people assume that AI systems—whether neural machine translation (NMT) or large language models (LLMs)—consistently deliver flawless results. But even texts that appear perfect at first glance can contain serious issues, such as mistranslated technical terms or legally problematic phrasing.
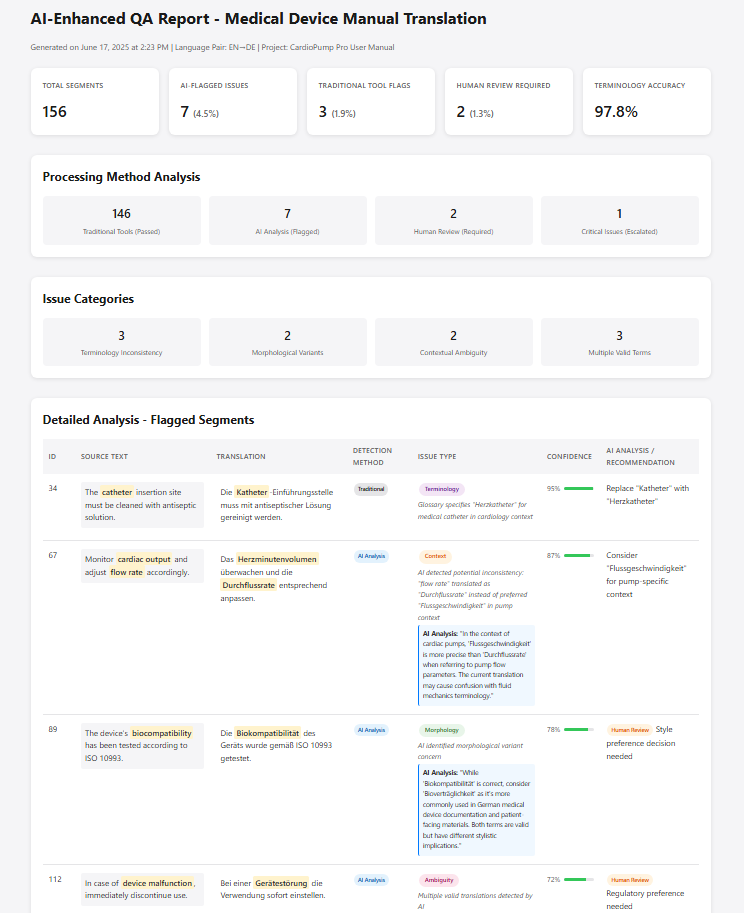
To avoid these risks, we rely on proven quality assurance methods. Using tools such as ErrorSpy and LookUp, we systematically analyze AI-generated translations to identify linguistic deviations and terminological inconsistencies. In addition, we create AI-supported review reports that highlight critical passages — making it clear where human expertise is still essential.
In this way, we combine the efficiency of AI with the precision of human professionals—ensuring reliable and scalable translation processes.
AI quality report
Machine translation and data security
Many companies rely on machine translation to securely process sensitive content such as confidential documents, legal texts or internal communications. However, using public online tools carries the risk of unintended data leaks – a scenario that no organisation should accept.
At D.O.G., we prioritise the protected and transparent use of AI. Instead of developing our own systems, we work with established, data protection-compliant MT and LLM solutions that can be seamlessly integrated into your secure workflows. For testing, prompt optimization, and simulations, we use locally hosted models on our GDPR-compliant server in Germany.
Your infrastructure, your control: You decide where and how the systems are deployed – whether locally in your data centre or in a secure cloud environment within Europe. We support you in implementing the right solution so that you always retain full control over your data.


Machine translation + post-editing according to ISO 18587
Many companies require machine translation solutions in conjunction with post-editing. While the current standard ISO 18587:2017 defines two levels of post-editing—light and full post-editing—the criteria for acceptable quality in practice vary greatly depending on the goals of the project and the machine translation engines used.
In real-world translation workflows, texts are often created using a combination of segments from a translation memory and machine translation. To ensure an optimal quality assurance process, it is crucial to have a clear strategy for the translation process labelling the origin of each segment. This makes it possible to assign the appropriate review method or post-editing step—whether the segment was human-translated or generated by MT.
We help you to define the optimum quality targets for your selected solution. Based on these targets, we develop clear guidelines and specifications for the work of your post-editing specialists.

Translation tools for machine translation
Human, DeepL or ChatGPT?
If you’re planning a trip to Rome, you have several transportation options. The same goes for machine translation. There is no one-size-fits-all system or approach, but several alternatives, depending on your content, data volume and budget.
So you can certainly choose between alternatives such as the following:
- Use of DeepL with company-specific glossaries
- Use of large language models that implement style and translation guidelines through individual prompts
- Combination of machine pre-translation (MT) and subsequent LLM optimisation
- We will be happy to advise you on additional options!
FAQ
These questions are often asked in connection with MT
Yes—especially when using free online translators. The risk of serious errors is greater with machine translations than with human translations. Some sentences read very well. However, important information is missing or a statement has been misinterpreted. These issues are not always recognized by inexperienced post-editors or those unfamiliar with the subject matter. By relying on trained post-editors, quality assurance tools, and terminology specifically optimized for machine translation, this risk can be significantly reduced—but never entirely eliminated. A decision in favour of MT must therefore also take these aspects into account.
The DIN ISO 18587 standard defines the requirements for post-editing and outlines the qualifications post-editors must meet. From a practical perspective, post-editing differs from revising human translations, even though the two processes share many similarities.
Depending on the desired quality level of the final output—whether light or full post-editing—post-editors must be able to suppress the instinct for perfection and focus only on necessary corrections. They also need to understand the specific types of errors machine translation systems tend to make, since machines may produce mistakes that humans rarely or never make—such as inserting content that isn’t in the source text.
This is why it is crucial to work with experienced service providers like D.O.G. GmbH, who are well-versed in the challenges and best practices of professional post-editing.
Technologies for successful machine translation
D.O.G. technologies support machine translation programmes
The success of machine translation solutions depends on the ability to detect translation errors and apply the correct specialised terminology. This is where D.O.G. offers distinct technological advantages. Since the company was founded 25 years ago, we have focused on developing software products that support the quality of our services. ErrorSpy and LookUp in particular help us to do this.
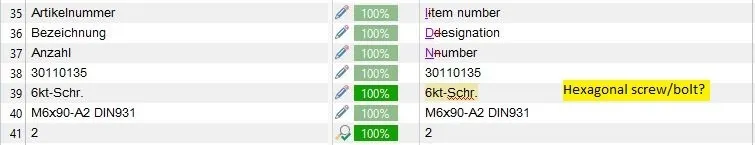
LookUp is an intelligent terminology management system. LookUp allows you to record relations between terms, providing valuable contextual information. Our software-supported checks take these relationships and your terminology into account. This means that our post-editors are better able to recognise machine-generated errors.
ErrorSpysupports post-editors in detecting and correcting machine translation errors:
- ErrorSpy can detect missing translations
- ErrorSpy reports terminology errors
- ErrorSpy checks the punctuation, the numbers, the consistency of the translation
- ErrorSpy also works with regular expressions. Typical machine translation errors can be stored as regular expressions and recognised automatically.
- ErrorSpy recognizes the context and can report incorrect translations in a specific context (e.g. when translating a word such as "performance").
The AI expertise of D.O.G.’s developers—combined with the ability to directly influence machine translation systems—is already delivering significant advantages. You can benefit from this, too.
Translation service in the field of AI translations
Automatic translation of your texts
Which texts are suitable for online translation with proofreading?
Not all content requires the same effort. With ourcontent matrix, we help you to categorize texts strategically and choose the right translation approach:
- Technical documentation: AI-supported pre-translation + specialist post-editing
(e.g. manuals, data sheets, specifications) - Marketing & website: AI + localization by native-speaking specialists
(e.g. Campaigns, claims, product pages) - Internal communication: Fully automated translation with basic check
(e.g. Emails, meeting minutes, newsletters) - Legal content: Traditional human translation
(e.g. Contracts, terms and conditions, compliance documents)
This matrix is not a rigid rulebook – but a pragmatic compass for making economically sound decisions.

Would you like to benefit from the advantages of machine translation?
Why not get in touch with us? We’d be happy to explore how automated translations can support your goals—no strings attached.